Background
Sex differences in phenotype presentation, disease trajectory and treatment response in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) have been reported. Nevertheless, whether classes of targeted therapies differentially affect men and women with PsA remains unclear.
Objectives
The objective was to assess the effect of sex on the long-term persistence of each class of targeted therapies in PsA.
Methods
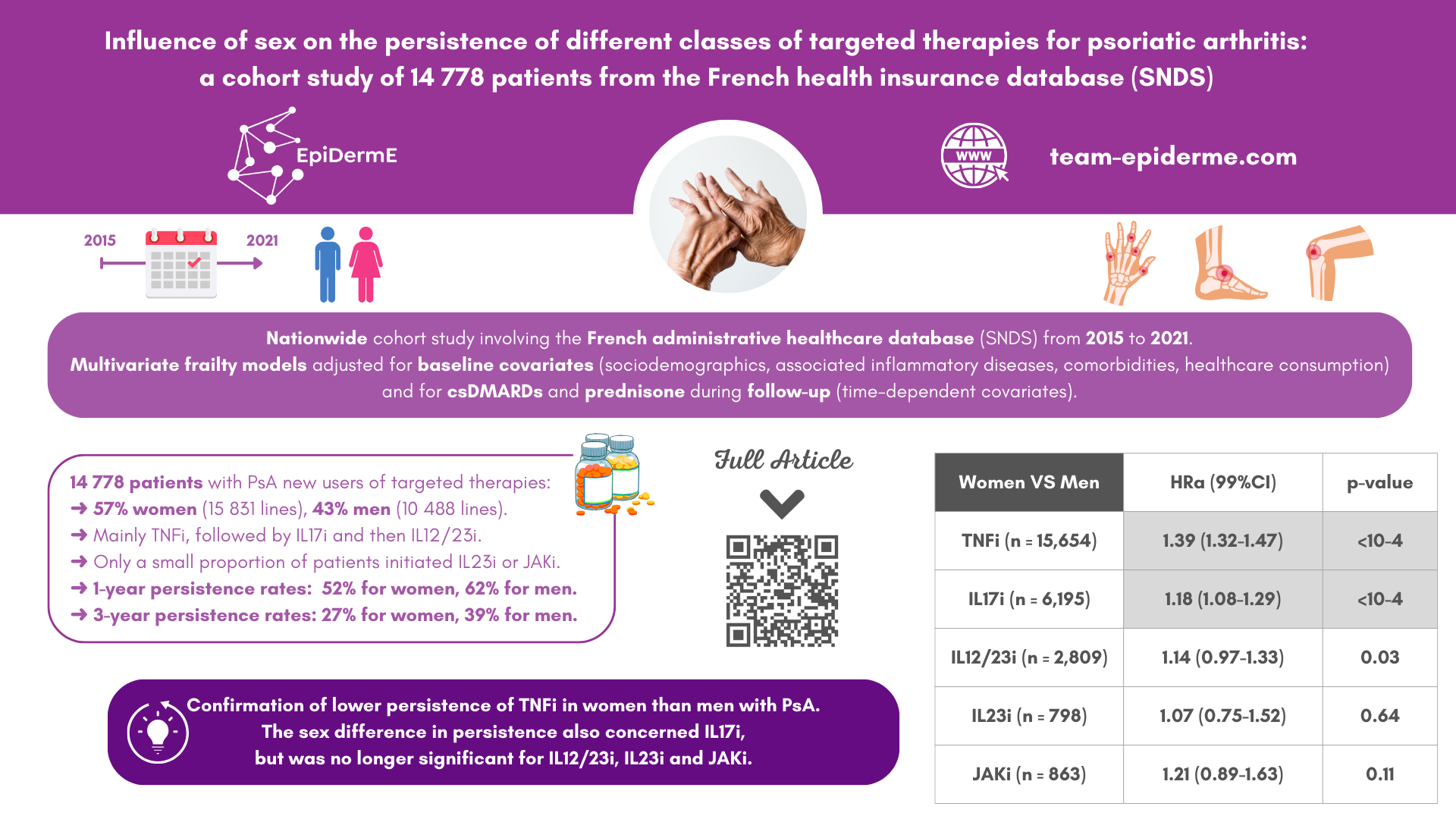
This nationwide cohort study involved the administrative healthcare database of the French health insurance scheme linked to the hospital discharge database. We included all adults with PsA who were new users of targeted therapies (not in the year before the index date) during 2015–2021 and studied all treatment lines during the study period. Persistence was defined as the time from treatment initiation to discontinuation and was estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method. Comparison of persistence by sex involved multivariate frailty models with conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and prednisone as time-dependant variables.
Results
We included 14 778 patients with PsA who were new users of targeted therapies: 8475 (57%) women (mean age 50±13 years; 15 831 lines), 6303 (43%) men (mean age 51±13 years; 10 488 lines). Overall, 1-year persistence was 52% for women and 62% for men and at 3 years it was 27% and 39%, respectively. After adjustments, persistence was lower for women than men for inhibitors of tumour necrosis factor (TNFi) (adjusted HR (HRa) 1.4, 99% CI 1.3 to 1.5) and interleukin 17 inhibitor (IL17i) (HRa 1.2, 99% CI 1.1 to 1.3) but not IL12/23i (HRa 1.1, 99% CI 0.9 to 1.3), IL23i (HRa 1.1, 99% CI 0.7 to 1.5) or Janus kinase inhibitor (JAKi) (HRa 1.2, 99% CI 0.9 to 1.6).
Conclusion
The treatment persistence was lower for women than men for TNFi and IL17i but not for IL12/23i, IL23i or JAKi.
- Psoriatic arthritis is a heterogeneous condition.
- Sex differences in phenotype presentation, disease trajectory and treatment response in PsA have been reported.
- In PsA, treatment persistence was lower for women than men, but with different magnitude by therapeutic class.
- The sex difference in persistence was significant for inhibitors of tumour necrosis factor and interleukin 17 inhibitor (IL17i) but not for IL12/23i, IL23i or Janus kinase inhibitor.
- This finding highlights the need for sex-based and gender-based studies to better understand the underlying mechanisms.
- Head-to-head studies with sex-stratified analyses are needed to tailor patient management and enable personalised medicine.
Influence of sex on the persistence of different classes of targeted therapies for psoriatic arthritis: a cohort study of 14 778 patients from the French health insurance database (SNDS)
Laura Pina Vegas, Laetitia Penso, Emilie Sbidian, Pascal Claudepierre
RMD Open. 2023 Dec 19;9(4):e003570.
doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003570. Online ahead of print. PMID: 38114199.